- Polka Dot Begonia: What Can You Do To Keep This Plant Healthy? - September 14, 2021
- Ficus Microcarpa: Why Is This A Must Have Plant? - September 13, 2021
- Begonia Ferox: How Long It Takes For Begoniaceae To Sprout? - August 24, 2021
As a tuberous Begonia with tiny orange-red flowers, Begonia Boliviensis (Begonia boliviensis A.D.C.) is a native of Southeast Asia, Africa, South, and Central America. The plant’s bloom time is late spring through summer.
How to Identify Begonia Boliviensis
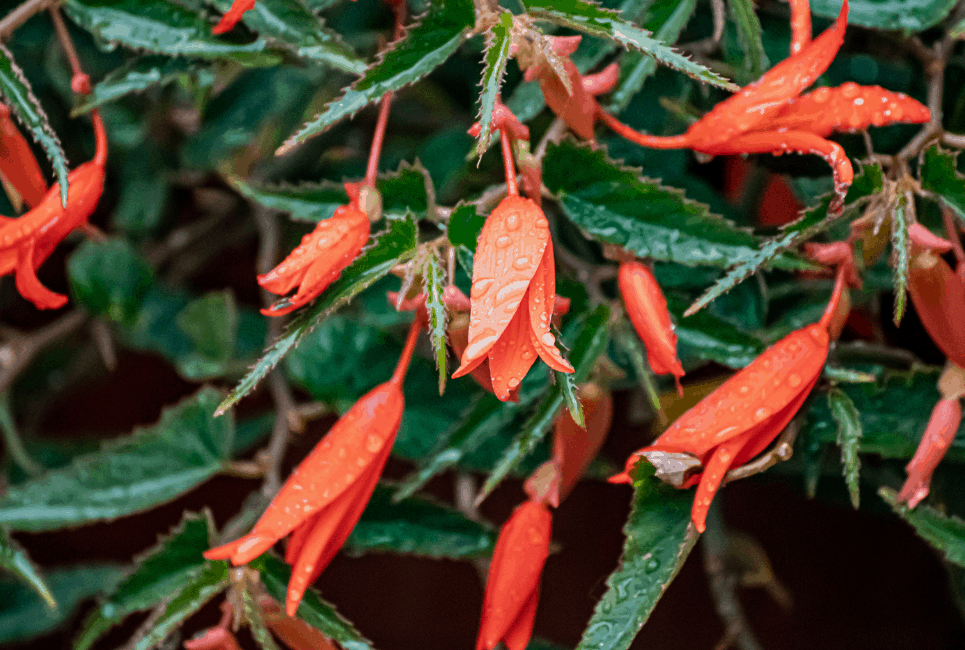

Begonia Boliviensis has tiny orange-red flowers as a tuberous Begonia with stems growing up from a tuberous rootstock, which is about 18 inches.
Flower production is in pairs and is composed of four-pointed segments. They are also in the angles of the obliquely lanceolate leaves when in three short stems. It has bell-shaped, bright-orange flowers that cover Begonia Boliviensis from the late spring to summer. A red margin typically serrates its foliage, and while it reaches about two feet tall, Begonia Boliviensis favors sunny locations.
How to Grow Begonia Bolivensis from Seed
A bit of professionalism might be required when growing Begonia Boliviensis from seed. However, virtually anyone can grow a seed. While it needs a lot of patience, some skill, or reasonable sterile conditions, it is not complicated at all. Consequently, you can see a little miracle happening. It will also be easy to grow a seed into mature plants when you follow the steps below.
Begonia Boliviensis seeds are some of the easiest varieties to grow. Growers can also sow them as easily indoors as they can outdoors. Begin seeds indoors six to eight weeks before the final frost for the earliest blooms. Afterward, you can transplant to outdoor or indoor with a partially-shaded spot.
The seeds may take around 21 to 28 days to germinate when it gets full lighting. Therefore, partial shade to full shade in well-drained, moist, and moderately fertile soil around 18-inches apart is also crucial.
How to Propagate Begonia Boliviensis
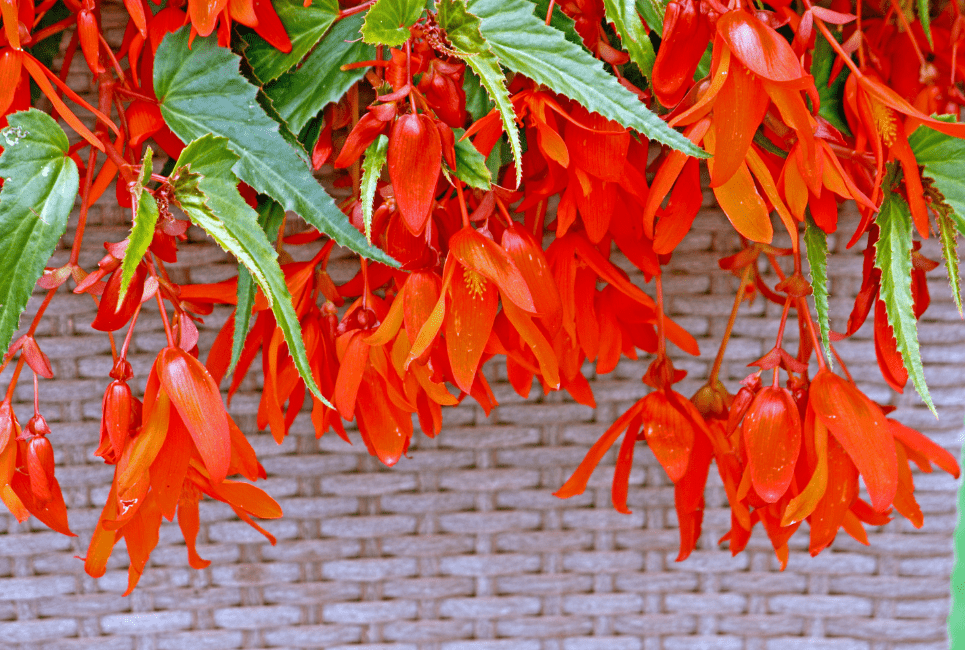

There are two ways to propagate Begonia Boliviensis: propagation from rooted cuttings and propagation from unrooted cutting.
Thus, it is critical to calculating 5 to 7 weeks with one plant in a pot for 4 to 5-inch pots when starting from an unpinched, rooted liner. Next, calculate about 8 to 10 weeks with four to five plants per pot for 10 to 12-inch baskets. Finally, pinch twice to finish with about 7 to 9 weeks using two plants per pot for gallons.
Ensure to use a rooting media; thoroughly water rooted cuttings, and slightly moisten finish media before transplanting. Allow the plant in a one-liner to be deep enough so that the media and rooting media level in the container. Ensure to maintain day temperature of about 65 to 75 degrees and night temperature of around 56 to 60 degrees after roots develop. Maintain 70 percent humidity all through.
For further finishing points, here are a few critical steps:
- Alleviate problems with soil porosity, air circulation, pH, and proper water management.
- After transplant to about three nodes, pinch a week after and not let the plant result in dormancy when it develops its fifth node.
- Promote compact growth through about 4,000-foot-candles of high light levels.
- Help prevent diseases by providing horizontal airflow.
When propagating from unrooted cuttings, it is crucial to put the cuttings in a disinfected propagation spot when they arrive. Use aerated, well-drained, and slightly moistened rooting media with a 1.0 to 1.5 EC and 5.8 to 6.2 pH. You can use preformed pots or paper and avoid direct contact between soil and foliage when sticking. The professional recommendation is bottom heat.
Uniform and quick rooting can come by 70 to 80 percent humidity, air temperature of 68 to 74 degrees, and media temperature of 72 degrees. When cuttings are well-rooted, you can lower the temperatures. However, they must not fall below 58 degrees.
When you are done with sticking, water cuttings slightly, avoid saturating media by misting for one to three days. Allow wilt slightly between mists as you keep cuttings somewhat dry. Run-offs can cause fungal issues and leach nutrients. Therefore, avoid it! Cover cuttings using cheesecloth and mist by hand only if possible. There will be root visibility after about 9 to 11 days, and you can expect between 21 to 29 days for the complete rooting time.
Begonia Boliviensis Growing Conditions
When growers place Begonia Boliviensis in ideal conditions, the plant will have a moderate growth rate. It can grow to around 12 to 18-inches in height and spread to about one to two inches.
It is critical to place Begonia Boliviensis in its favorable setting to produce its somewhat pointy green leaves and characteristic reddish-orange blooms. It can lead to slow or disorganized growth when failed to do so.
Begonia Boliviensis’ flowers are composed of four-pointed segments and sprout in pairs or three stems. The plant’s leaves have elongated appearances that give Begonia Boliviensis a classy and elegant look. Its beautiful scarlet fiery-red blooms are the result of its popularity. In addition, it gives it an eye-catching and striking combination with its neatly serrated, arrow-shaped green foliage.
How to Plant Begonia Boliviensis
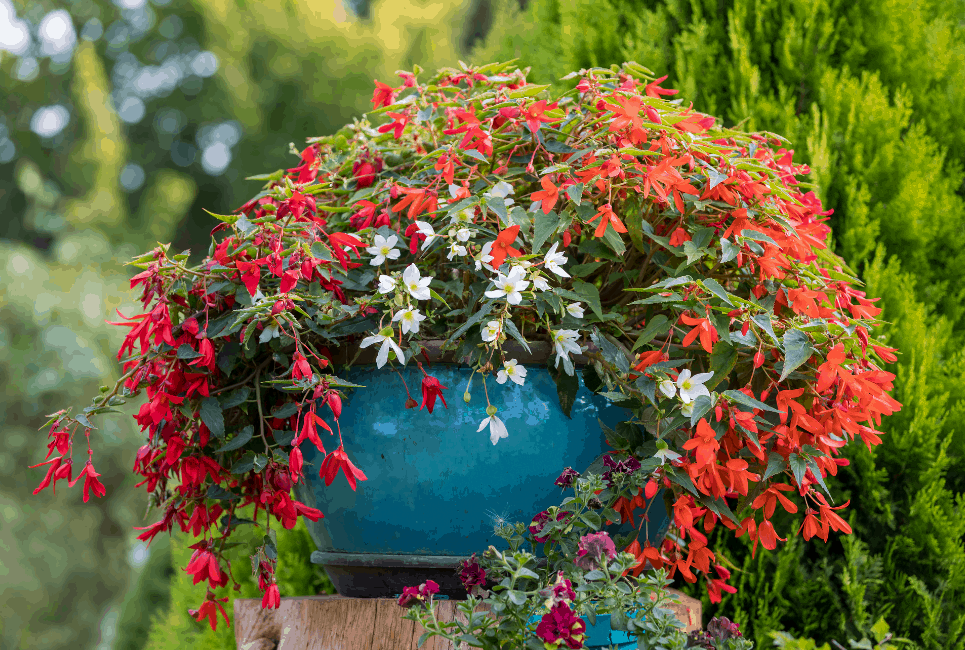
Begonia Boliviensis is an easy-to-grow plant used in clumps in frost-free gardens with a Mediterranean climate, tropical and subtropical, and indoor plants in hanging pots. The plant can grow in sunny or semi-shady exposures as its bronze-leaved species are suitable for full sun. However, it may produce fewer flowers and grow less when grown in full shade. Begonia Boliviensis can withstand 3 to 5 degrees temperatures but not frost.
When you want to plant your Begonia Boliviensis, you will need:
- Potting container
- A pair of scissors
- Rooting powder
- Fertilizer
- Water
- Healthy Begonia Boliviensis plant
Night plant before planting, water the plant’s parent plant so it can hydrate its foliage and stems. After that, do the following:
- Use an equal perlite mix and milled peat or coir to fill a 4-inch container. Moisten thoroughly after putting some water. Then, wait for the excess water to drain from the pot for about thirty minutes.
- Choose long stem cutting of about 4 to 6-inch long. This stem must be less than ¼-inch in diameter without flowers. Therefore, an unhealthy or damaged stem is not an option.
- Use clean scissors to cut about 1/8-inch of the chosen stem cutting below a pair of leaves.
- Ensure that you have removed leaves at the lower part of the stem cutting. Remember also to cut away any buds or flowers.
- Next is to put the stem cuttings severed end into rooting hormone or powder. Then, get rid of the stem-cutting by gently blow on the immersed end.
- Ensure that the hole you will make in the prepared potting mix is deep enough to hold the stem cutting’s lower half.
- You can now place your hormone-coated plant’s end into the planting hole. Ensure that the stem can hold the cutting firmly by carefully pushing the potting mixture around it. Water the base to settle the prepared potting mix and to further upright.
- Look for the bright-indirect sunlight spot to place your potted stem-cutting. The preferred spot can be a partially-covered outdoor patio or a lightly shaded window.
- Let the stem-cutting have sufficient hydration by ensuring to mist it every day. Ensure moisture soil. However, the young plant can rot easily. As such, avoid overwatering.
You can lightly tug on the stem’s base after about two weeks to check if your Begonia Boliviensis has developed roots. It is also worth checking if the cutting’s roots have been anchored to the potting mixture. The next step is to take it into a 6-inch pot after two more weeks. Ensure to fill the pot with more potting soil.
Begonia Boliviensis Potting & Soil
Begonia Boliviensis thrives well with rich, loamy, and well-draining soils. A soil-less mixture precisely prepared for indoor plants would be a perfect choice. Growers can have their Bonfire plant grow well enough when their soils provide an excellent medium or contain perlite, vermiculite, and peat moss. My recommendation is to stay away from using amendments like garden soil or compost.
Your plant will like neutral soil of 6.6 to 7.5 and slightly acidic soil of 6.1 to 6.5. However, Begonia Boliviensis can grow in faintly alkaline soils and tolerate a wide range of soil pH, an admirable trait of the plant. However, ensure to use well-draining and moist neutral or acidic soils for the best growth.
There is always a need for consistent watering regarding many Begonia variations’ soils like Begonia Boliviensis. However, you can have a case of stem’s water-logging with overwatering. Thus, you can water your plant when you notice that its soil is somehow dry.
Ensure that only a few inches of the soil top dry out and not the whole plant because it can be significant damage when the plant dries out excessively.
Regarding repotting, Begonia Boliviensis does not need constant repotting, even though it has considerably large leaves and blooms. Instead, you can repot every two years to a larger pot and ensure a considerable space for the roots to grow and the container has good drainage.
Begonia Boliviensis Water Requirements
Regular watering of your Begonia Boliviensis is appropriate. However, you may have to deal with fungal infections and root rot when you overwater. Therefore, it is essential to check the soil to determine when to water your plant. You can water the plant when you notice that about one to two inches of the topsoil is dry. However, leave the plant for some time if the soil appears to be sufficiently watered or moist.
Balancing between the two extremes of overwatering and underwatering is quite essential. Ensure to water as required. Begonia Boliviensis can thrive well and develop healthily with water. Thus, it is critical to avoid the extreme ends of overwatering and underwatering.
When watering, use lukewarm water that has low chlorine. With this, you can prevent your plant from temperature shock and toxicity. Next, fill a container with some water and leave it for 24 hours if you can access chlorinated water only. When you see that some chlorine has escaped, water your plant with it.
Begonia Boliviensis Light Requirement
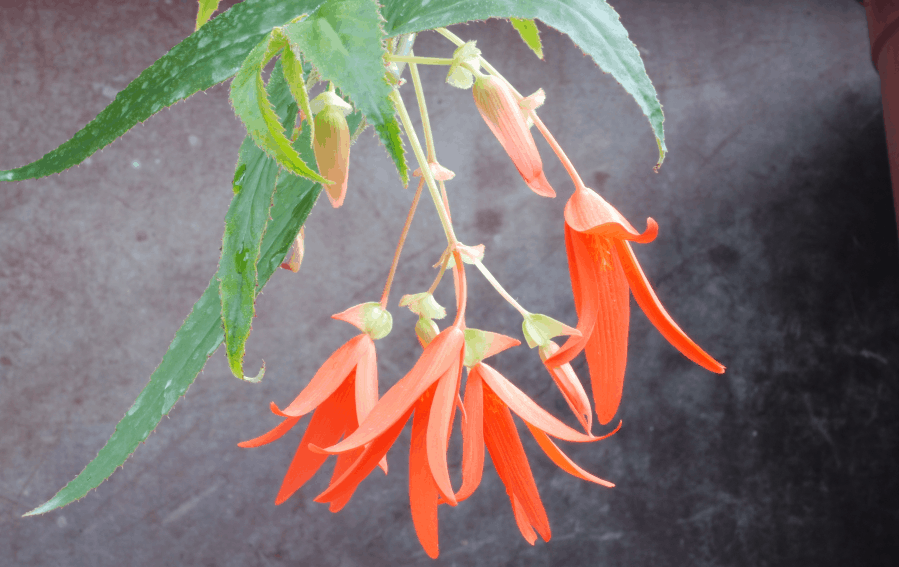

Begonia Boliviensis is a plant that loves flecked bright sunlight. However, when exposed to direct sun’s harsh rays, it can result in leaf-scorching. Therefore, placing Begonia Boliviensis in the protective indoors is an ideal choice regarding light.
Place your Begonia Boliviensis where filtered; indirect light hits the plant if you plan to grow it indoors. Typically, such a light-sensitive plant will enjoy the best sunlight from southwest-facing windows. However, the plant can also enjoy the partial sun that comes into contact with it when placed on your balcony.
However, your patio can be an ideal choice if you plan to grow Begonia Boliviensis outdoors. It is recommended to ensure that your plant remains in the partial sun all the time. As an option, artificial growing lights are also perfect for growing the plant.
Best Begonia Boliviensis Fertilizer

It may require some work for any grower to see cheerful, bright blooms hanging from their Begonia Boliviensis. But, as an enthusiast, you can achieve that by feeding your plant with high nitrogen fertilizer for rapid growth.
Some of the best products specifically designed for Begonias are these high-quality plant fertilizers. When your plant is in the growing season of spring and summer, use a consistent diluted t powder fertilizer for about three weeks for optimal growth.
However, it is highly recommended to reduce the fertilizer application once a month in the late autumn season. Also, stop adding any fertilizer altogether when the winter arrives. It is because colder seasons are not ideal for Begonia Boliviensis’ active growth.
Ensure that you don’t over-fertilize or starve your plant. While adding excess fertilizer may lead to nutrient toxicity, your Begonia Boliviensis may suffer significant slow growth when you starve it. Since these two are quite dangerous, you may need to adhere to a similar feeding schedule the following spring.
Best Begonia Boliviensis Companion Plantings
While people grow Begonia Boliviensis for its multicolored leaves and colorful flowers, having companion plants can take advantage of increased humidity when you plant them closer together. Here are some plants that echo your Begonia Boliviensis with similar growing requirements.
Begonia Boliviensis and Yellow Corydalis
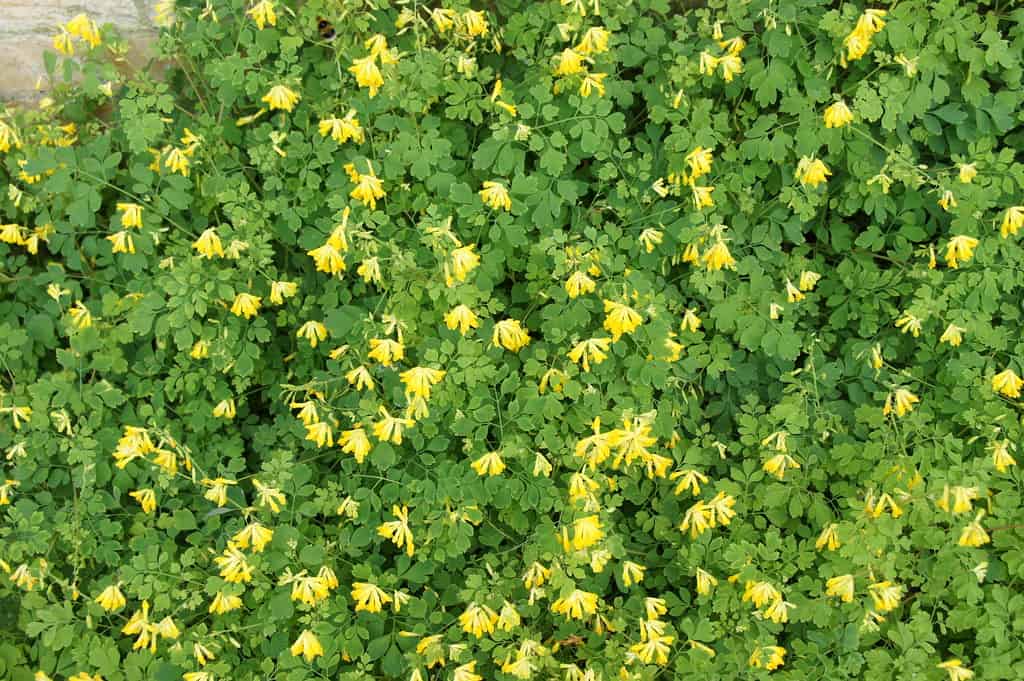

Begonia Boliviensis lives well with this bright-colored Yellow Corydalis (Corydalis Lutea). The plant forms a 12-inches wide of golden yellow flowers and pale green.
Light Requirements
Yellow Corydalis needs partial shade or full sun.
Soil Requirements
The plant thrives well in organically rich, well-drained soil. Yellow Corydalis also loves alkaline or neutral pH soil.
Water Requirements
Yellow Corydalis grows well in moist soil, and it is essential not to allow the soil to dry out completely between watering.
Pros
- Self-seeds and an aggressive grower
- Light-green, bright, and ferny foliage
- Beautifully-divided leaves
Cons
- The plant is intolerant of hot and humid summers
- Does not respond well to transplanting
Begonia Boliviensis and Dwarf Elephant’s Ear
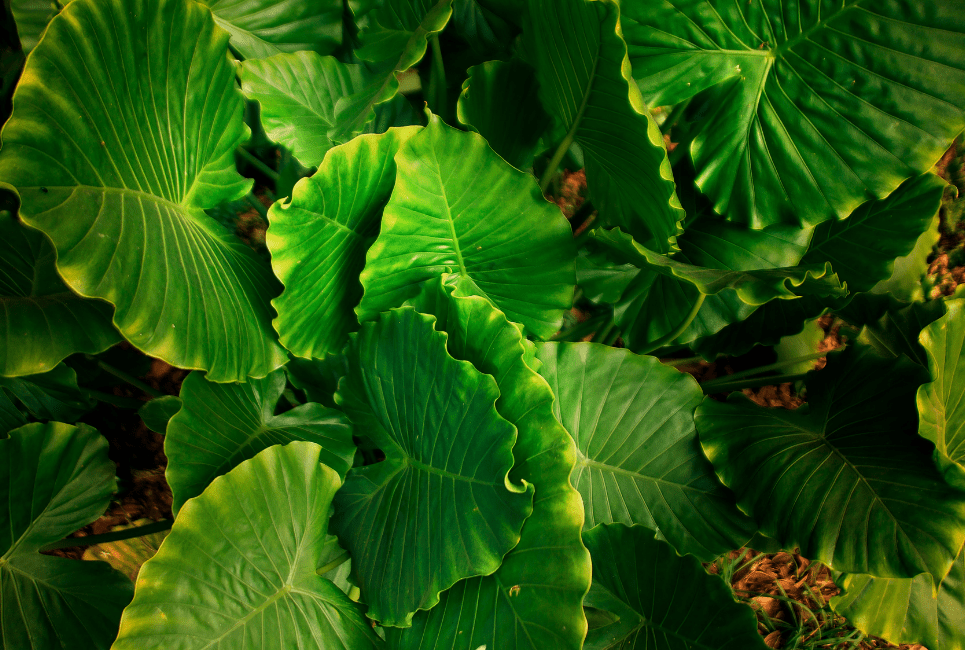

Dwarf Elephant’s Ear (Colocasia Afienningsii) is another companion planting with Begonia Beloviensis since growers can match bronze and green colors of their Begonia with this plant.
Light Requirements
Dwarf Elephant’s Ear can thrive well in a place with partial shade or full sun.
Soil Requirements
This plant requires well-drained, unsaturated, and rich soil.
Water Requirements
Growers can water their Dwarf Elephant’s Ear plants when the soil feels a bit dry.
Pros
- The plant makes a perfect landscape plant
- Easy to grow indoors
- Lots of fun to grow
Cons
- Less considerable growth when planted indoors
- The plant’s stems and leaves contain oxalic acid
Begonia Boliviensis Diseases and Common Problems

Slugs and snails are some of the issues Begonia Boliviensis growers face. While this issue is not as frequent as others, your plant can be susceptible to sporadic attacks. Humid and wet nights are suitable settings for slugs and snails as they feed mostly on decaying plant stems and leaves.
You may need to check silvery trails that look like gold dust on Begonia Boliviensis when looking if these insects have infected the plant. It is possible slugs and snails have attacked your plant if you see this type of trail.
There’s a possibility of seeing some holes in Begonia Boliviensis leaves with the base of baby leaves chewed off. Get rid of any pots, pipes, rocks, or similar decorations you have close to the plant to clear off the slugs and snails. These may serve as daylight shelter for the snails.
Whiteflies
Whiteflies damage many plants, such as the Begonias. These insects disrupt a healthy plant with their continuous appearance. You can shake your Begonia Boliviensis and then wait for a few moments if you want to see if these insects have infected the plant. You will see the whiteflies swarming in the air if they are hiding in it.
Their preferred residence is beneath the leaves’ area. As such, you may have a hard time finding them initially. Therefore, they might have incurred significant damage when you notice a problem. These insects weaken your plant by feeding on its nutrients, making it more prone to other conditions. They can even attract other insects to your plant by leaving behind honeydew.
You can get rid of these insects using insecticidal soap or spray.
Aphids
Aphids are a common Begonia Boliviensis attacker. You will see these insects as clusters around your plant’s flower buds and young shoots. They can also hide under its old foliage. Your plant’s leaves can bend at unusual angles or twist upon themselves when aphids infect them.
These insects can also slow down new growth considerably. Aphids can even produce a honeydew substance that worsens the situation since sooty mold fungus can thrive well in this environment. This situation can affect your plant significantly.
An instant fix to eliminate aphids is to use insecticidal soap or spray. First, it is essential to thoroughly wash Begonia Boliviensis and mist it to eliminate these insects.
Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is one of Begonia Boliviensis’s most common problems. You can expect this fungal infection on your plant when you expose your Begonia to excessively dry conditions or high humidity for so long.
Powdery mildew is like an ash-grey or white film that mostly affects older foliage or on your plant’s leaves’ lower or upper surfaces.
Powdery mildew can also disrupt your Begonia Boliviensis’s overall arrangement while also limiting new growth. The case can even result in leave blackening. In addition, the flower buds may not open because of the infection severity.
Fortunately, it is easy to deal with this situation. First, wash your Begonia Boliviensis’s leaves with insecticidal soap. You can also use the insecticidal spray on your plant often or plant it in a pasteurized potting medium to prevent any infection.
Begonia Boliviensis Treatments and Maintenance

Begonia Boliviensis requires little maintenance, and with proper culture and care, you can easily prevent many common diseases. One of the best maintenance you can give your plant is to avoid getting its foliage wet since this can lead to bacterial leaf spots and other diseases.
You can also have fungal root diseases issues in hand when you use soil that doesn’t drain properly. Therefore, don’t overwater your plant. Essentially, Better Homes & Gardens recommends that growers must allow the soil to dry before watering their plants again.
Also critical is proper air circulation with your plant to prevent powdery mildew. When you grow the plant in an environment with too much humidity, there is a possibility of botrytis blight cases. When growing Begonia Boliviensis indoors in window boxes or hanging baskets, good ventilation is critical. And remember that too much light can burn the leaves and flowers, even though the plant can grow in full sun.
Where to Buy Begonia Boliviensis Seeds Online
Begonia Boliviensis seeds are available online at:
Where to Mature Buy Begonia Boliviensis Online
Begonia Boliviensis is an easy-to-grow, showy, and deer-resistant plant with a stand-out variety that won’t stop when it starts growing. You have different places to buy your mature plant online, and some of them are:
FAQs
Question: For how long does a Begonia Boliviensis live?
Answer: Begonia Boliviensis can live for about two to three years with adequate care and maintenance.
Question: How often do Begonia Boliviensis plants bloom?
Answer: Begonia Boliviensis plants bloom from spring to fall.
Question: Are Begonia Boliviensis plants toxic?
Answer: The plant tends to be toxic to animals. As such, it is crucial to keep Begonia Boliviensis away from infants and pets.
Conclusion
Begonia Boliviensis has colorful and unique foliage and blooms as a beautiful species. The plant has fiery red blooms that can light up any dullest rooms. It is also easy to care for this plant. On the other hand, this plant is poisonous to animals. Thus, ensure that they are not close to animals and babies.

